Open
the Hyper-v Manager, right-click Hyper-v Server and select Edit Disk; or in the
Actions pane,select Edit Disk.
Click Next
Click Browse to select
the virtual disk you want to change, then click Next.
Select the action you
want to perform. You can do the following:
Compact: Reduces the
size of a dynamically expanding or differencing disk by deleting empty space,
while leaving the disk’s capacity unchanged.
Note:
After the file is delete in the dynamic hard disk, the size of the hard disk
file will not chang. For example,a dynamic hard disk
file has 20GB, I copied a 10GB file to the hard disk, this moment the size of
the hard disk file is 30GB, when I delete the 10GB file in this hard disk, the
hard disk file size still 30GB. At this point you need to use Compact.
Convert: Creates a copy
of the disk image file, enabling you to change the format (VHD or VHDX) or the
type (fixed size or dynamically expanding) in the process.
Expand: Increases the
capacity of the disk.
Shrink: Reduces the
capacity of the disk by deleting empty storage space from the file. The option
only appears when there is unpartitioned space available at the end of the
virtual disk.
Note: When the virtual machine is running only Expand and shrink options are available.
Merge: combine the data
on the differencing disk and its parent disk to form a new file. The option
only appear when you select a Differencing disk.
In this example, I
chose Expand. Then click Next.
Type new virtual disk
size in the New Size text box. Then click Next.
Click Finish
You
can use the Optimize-VHD cmdlet
on Windows PowerShell to compact a virtual hard disk file.
You can use the Convert-VHD
cmdlet on Windows PowerShell to convert a virtual hard disk file. Form a VHD
file to a VHDX file, from a fixed size file to a dynamic file or from a fixed
size VHD file to a dynamic VHDX file.
You
can use the Resize-VHD cmdlet on Windows PowerShell
to expand or shrink a virtual hard disk size.
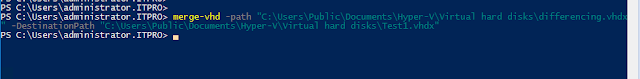
You
can use the Merge-VHD cmdlet on
Windows PowerShell to merge a differencing disk into its parent disk.